Our Approach
Unleashing the full potential of immuno-oncology therapies
Immuno-oncology (I-O) therapies have demonstrated curative potential for people living with cancer. However, their use to date has been significantly curtailed due to systemic toxicity caused by activity of the therapeutic molecule outside of the tumor microenvironment (TME).
Xilio is discovering and developing novel biologics to improve upon existing I-O mechanisms and deliver an improved efficacy-to-toxicity ratio, or therapeutic index. We are advancing a pipeline of novel clinical and preclinical immunotherapies designed to achieve tumor-selective activation, including masked bispecifics and masked T cell engagers.
Our Platform
Xilio has developed a proprietary, clinically validated platform technology to engineer tumor-activated biologics. Each of our molecules leverages masking and other unique components that are designed to be optimized for the specific target to focus therapeutic activity within the TME.
Our platform’s masking approach aims to limit therapeutic activity in the periphery and enables selective activation of the molecules within the TME. There, matrix metalloproteases (MMPs)—enzymes essential for tumor growth and metastasis—cleave and separate a linker that connects the masking domain to the active agent. This process is intended to allow the therapeutic molecule to activate fully within the TME and directly target cancer cells.
Systemically Active
Immunotherapies
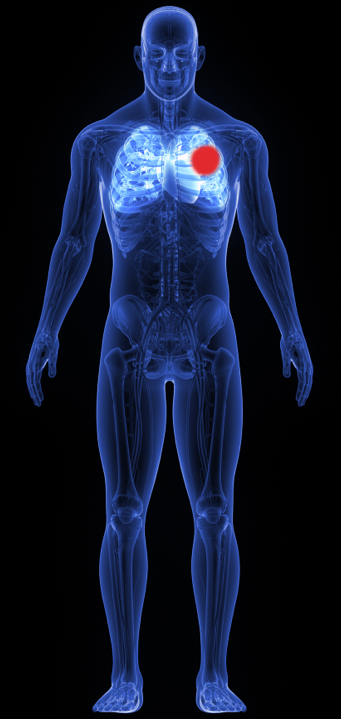
Lung Cancer Example
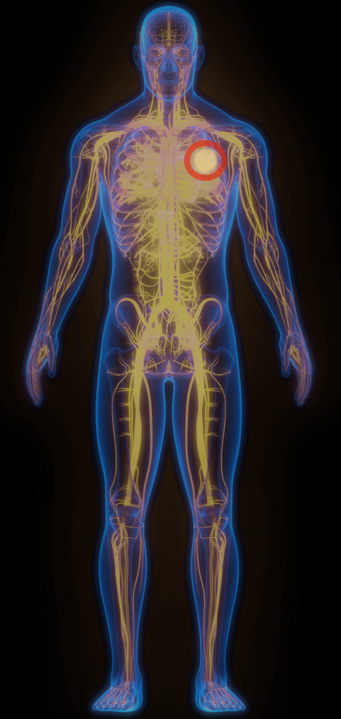
Xilio Tumor-Activated
Immunotherapies

Lung Cancer Example